
In today’s fast-paced digital era, artificial intelligence (AI) has become a cornerstone of modern software development. Among the most transformative tools in this space are Large Language Models (LLMs), which are revolutionizing the way developers write and interact with code. From generating entire code snippets to offering intelligent code suggestions, LLMs have drastically reduced development cycles and boosted productivity. However, with this advancement comes an undercurrent of risk: the threat of LLM poisoning.
What Is LLM Poisoning?
LLM poisoning is an emerging cybersecurity threat in which adversaries intentionally introduce malicious or misleading data into the training datasets of large language models. This can also include exploiting weaknesses in model fine-tuning or prompt-handling mechanisms to manipulate outputs. The consequences of such manipulation are severe: poisoned LLMs can generate insecure code, embed hidden backdoors, or include malicious logic in otherwise seemingly legitimate code suggestions.
The danger is particularly acute in AI-powered development environments where developers rely on LLMs to generate boilerplate code or solve complex algorithmic challenges. A single poisoned suggestion that goes unnoticed can propagate vulnerabilities across multiple systems, leading to compromised software and security breaches.
The Implications for Software Security
The infiltration of malicious logic via LLM poisoning is not just a technical nuisance. It introduces far-reaching implications for application security, regulatory compliance, and brand reputation. Organizations that unwittingly deploy software containing code generated by compromised LLMs face the possibility of:
- Systemic vulnerabilities that can be exploited at scale.
- Intellectual property theft or data leakage is a huge problem.
- Violations of regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Loss of customer trust due to security incidents.
Traditional AppSec approaches, which rely heavily on post-development scanning or manual code reviews, are not equipped to handle this type of attack. These methods detect vulnerabilities too late in the development process, often after the damage has already been done.
How does Checkmarx One Assist – Agentic AI AppSec Platform Help?
Checkmarx addresses this critical gap with our innovative Agentic AI Application Security (AppSec) Platform, a next-generation security solution purpose-built to safeguard modern, AI-assisted software development.
The Agentic AI platform integrates seamlessly into the entire software development lifecycle (SDLC), from initial coding in the IDE (VSCode, Cursor, Windsurft, etc.) to final deployment. It continuously scans and monitors code, offering proactive identification and remediation of vulnerabilities in real time. This includes identifying code anomalies, dependencies on malicious packages, secrets, and potentially poisoned suggestions that stem from compromised LLM interactions.
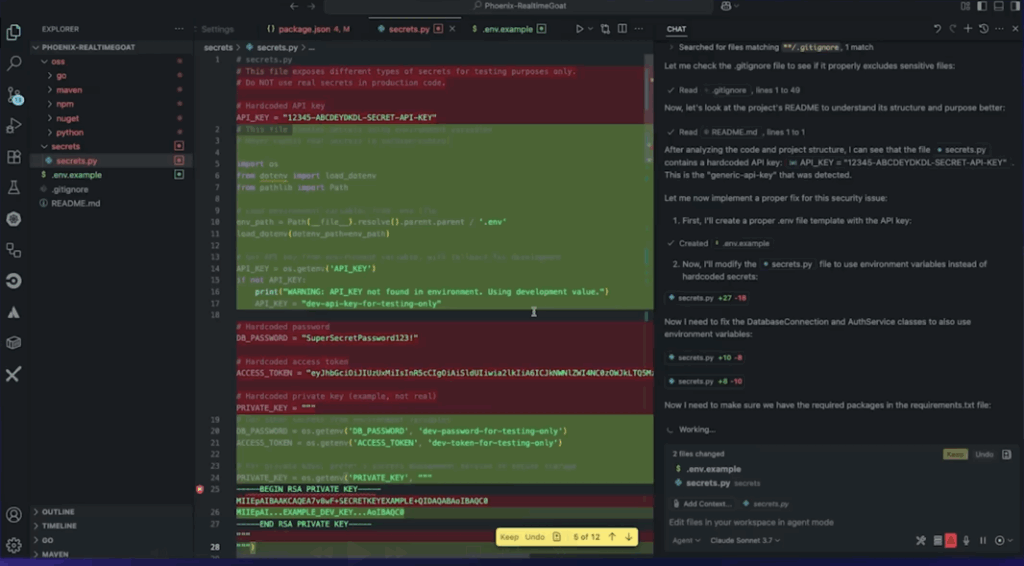
With the rise of these OWASP also created and continuously maintains the Top 10 LLM https://owasp.org/www-project-top-10-for-large-language-model-applications/
Among the threats that are being covered in the OWASP LLM Top 10 (LLM 01-LLM 10) nowadays are:
1. Prompt Injections
Malicious users manipulate inputs to override or alter the LLM’s intended behavior, leading to unexpected or unsafe outputs.
2. Sensitive Information Disclosure
The model unintentionally reveals confidential data, such as credentials, internal logic, or personal information.
3. Supply Chain LLM Risks
Using outdated, unvetted, or deprecated models can introduce vulnerabilities inherited from third-party sources.
4. Data and Model Poisoning
Attackers corrupt training data or fine-tuning inputs to insert backdoors, bias outputs, or degrade security.
5. Improper Output Handling
Failure to validate or sanitize LLM responses can lead to unsafe actions, injection attacks, or misinformation propagation.
6. Excessive Agency
LLMs with too much autonomy or access (e.g., to file systems or APIs) can take actions beyond their intended scope, introducing serious risks.
7. System Prompt Leakage
System-level instructions meant to govern the LLM’s behavior become visible to users, enabling manipulation or bypassing safeguards.
8. Vector and Embedding Weaknesses
Flaws on how inputs are converted to embeddings (for similarity search or retrieval) can be exploited for poisoning or inference attacks.
9. Misinformation
LLMs may confidently generate false or misleading information, which can be especially damaging in regulated or high-stakes domains.
10. Unbounded Consumption
LLMs can overuse system resources (e.g., compute, memory, API calls), leading to denial of service or cost overruns when limits are not enforced.
For this reason, The OWASP AIVSS project created a framework to quantify these new risks, called AIVSS. It’s not a replacement for CVSS, but a critical extension that allows security teams to measure the full risk profile of Agentic AI systems.
You can read more about AIVSS in this article by OWASP member, Ken Huang.
Real-Time Defense at the Code Level
A standout capability of the Checkmarx Agentic AI platform is its ability to flag and fix security vulnerabilities as code is written, which is a critical feature when dealing with the rapid outputs of LLMs. Developers using AI-enhanced IDEs like Cursor or CoPilot, can benefit from instant feedback and remediation suggestions that are context-aware and security-focused.
This real-time defense mechanism drastically reduces the window of exposure. Rather than relying on security audits or penetration tests at the tail end of development, Agentic AI embeds security controls at the source—where LLM-generated code is created and integrated.
Each time a security threat is remediated, the Checkmarx Developer Assist agent automatically refactors the affected code to ensure it remains functional and compiles cleanly – seamlessly preserving the integrity of the CI/CD pipeline.
Behavior-Driven Threat Detection
Beyond traditional static and dynamic analysis across the Checkmarx One AppSec engines (SCA, Malicious Packages, Secrets, Containers, and more), Checkmarx’s Agentic AI leverages behavior-driven AI models that monitor usage patterns and execution behaviors to detect anomalies indicative of poisoning attempts. These capabilities include:
- Anomaly detection in code patterns that deviate from normal development behavior.
- Exploitability assessments to determine how vulnerable a particular code segment is in a runtime context.
- Reachability analysis to identify if an introduced vulnerability is exploitable.
This allows the platform to not only identify known threats but also anticipate and mitigate novel attack vectors that exploit the very nature of generative AI systems.
Empowering Developers Without Slowing Them Down
A key advantage of Agentic AI is its developer-first design. Security is often seen as a blocker to innovation, but Checkmarx aims to make it a silent enabler. By integrating with IDEs and CI/CD pipelines, the platform ensures that security checks and fixes occur naturally within the developers workflow. There is no need for disruptive context switching or cumbersome security gates that slow delivery.
Instead, developers are empowered with:
- Inline code suggestions that are secure by design.
- Alerts for suspicious behavior in third-party packages or dependencies.
- Automated remediation options for discovered issues.
This reduces the burden on AppSec teams while giving developers the confidence to move fast without compromising security.
Future-Proofing Software in the Age of AI
As AI continues to advance and LLMs become more deeply integrated into everyday development workflows, the risks of LLM poisoning and other AI-based threats will only increase. The future of secure software hinges on our ability to not only detect but also prevent such risks at machine speed.
Checkmarx One Assist Agentic AI AppSec platform offers enterprises the tools they need to stay ahead of the curve. By combining deep security expertise with innovative AI capabilities, it provides comprehensive coverage across the evolving threat landscape.
As teams adopt cloud-native architectures, microservices, rely more on vibe-coding and AI generated code techniques, Agentic AI supports the process by helping review and secure both human and machine-generated code.
Conclusion
The rise of LLMs has unlocked tremendous potential for innovation in software development. But with this power comes new vulnerabilities that traditional security approaches cannot address alone. LLM poisoning is a prime example of how attackers are evolving alongside the tools developers use.
To stay protected, organizations must embrace a new breed of security platforms, ones that are proactive, intelligent, and seamlessly integrated into the developer experience.
Learn about Checkmarx One Assist
Proactively protect software from AI-driven and software supply chain threats.